The most-read news items of the last week selected by the editors of “Il Brevetto Magazine”: Dullo, high-tech hockey, mushrooms and pain-relieving patches
What are the most-read news stories of the last week? What were the trending topics in the world of innovation? What was talked about on social networks around the world? In order to answer these questions, we have selected the news items that have had the most visibility on our portal over the past week and have aroused the curiosity of our readers. The most-read news item is about NHL high-tech hockey pucks, but there are also interesting articles for chemistry and medicine fans.
Most read news of the week
Mushroom-inspired ‘gentle’ Velcro
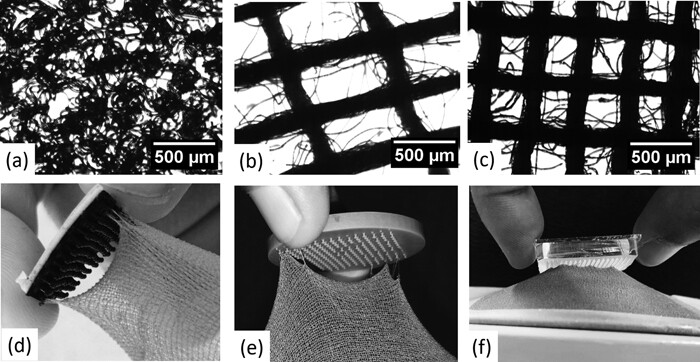 Researchers at Wageningen University in the Netherlands have invented a new, much longer-lasting Velcro adhesive material. The research was published in the international journal Biointerphases. The new fastening system is made using a 3D printer, which allows the classic rigid hooks to be replaced by soft plastic structures in the shape of tiny mushrooms. The new material, when pressed against a fabric, adheres thanks to the shape of the upper part of the mushrooms which is embedded in the fibres of the fabric. FIND OUT MORE
Researchers at Wageningen University in the Netherlands have invented a new, much longer-lasting Velcro adhesive material. The research was published in the international journal Biointerphases. The new fastening system is made using a 3D printer, which allows the classic rigid hooks to be replaced by soft plastic structures in the shape of tiny mushrooms. The new material, when pressed against a fabric, adheres thanks to the shape of the upper part of the mushrooms which is embedded in the fibres of the fabric. FIND OUT MORE
Sleep well thanks to Dullo
 Dullo could be the solution to all your problems, a multi-purpose headrest consisting of two pillows that makes it easier to sleep on your side, protecting your spine. More precisely, Dullo consists of two separate pillows attached to each other to form a multi-purpose padded headrest. It allows you to assume different positions while maintaining correct posture, because there is a concave side that gives your neck support to keep your spine in the right position if you sleep on your back. FIND OUT MORE
Dullo could be the solution to all your problems, a multi-purpose headrest consisting of two pillows that makes it easier to sleep on your side, protecting your spine. More precisely, Dullo consists of two separate pillows attached to each other to form a multi-purpose padded headrest. It allows you to assume different positions while maintaining correct posture, because there is a concave side that gives your neck support to keep your spine in the right position if you sleep on your back. FIND OUT MORE
Hockey: the NHL will use pucks equipped with sensors to collect data
 Technology is taking the field. Or rather, on the ice. The 2021 season of the NHL – the top American hockey league – will feature the use of real intelligent pucks. On the surface, the new pucks will be identical to the black rubber ones that have been used for decades. Inside, however, is a complex system of chips, sensors and circuit boards capable of collecting and sharing thousands of data. FIND OUT MORE
Technology is taking the field. Or rather, on the ice. The 2021 season of the NHL – the top American hockey league – will feature the use of real intelligent pucks. On the surface, the new pucks will be identical to the black rubber ones that have been used for decades. Inside, however, is a complex system of chips, sensors and circuit boards capable of collecting and sharing thousands of data. FIND OUT MORE
A pain-relieving plaster for wounds from the US
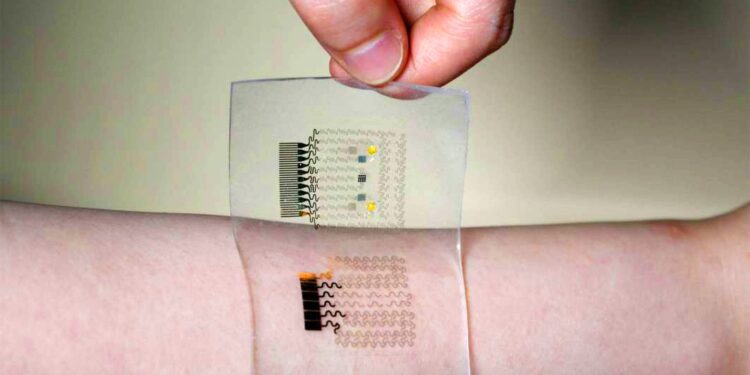 Researchers at Duke University (North Carolina) have developed a special pain-relieving patch that can be applied directly to post-operative wounds. The medical device provides a period of pain relief through the release of a non-opioid painkiller. Specifically, the patch releases a substance capable of deactivating Cox-2 (cyclooxygenase-2), an enzyme that plays a key role in generating the inflammatory reactions that underlie pain. FIND OUT MORE
Researchers at Duke University (North Carolina) have developed a special pain-relieving patch that can be applied directly to post-operative wounds. The medical device provides a period of pain relief through the release of a non-opioid painkiller. Specifically, the patch releases a substance capable of deactivating Cox-2 (cyclooxygenase-2), an enzyme that plays a key role in generating the inflammatory reactions that underlie pain. FIND OUT MORE