The great news comes from a Chinese study that confirms the presence of specific antibodies against the new coronavirus weeks after the appearance of symptoms
A bright light of hope during the emergency caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. A Chinese study, published in nature medicine, shown for the first time that COVID-19 patients develop specific antibodies against the virus. The researchers observed similarities between the new coronavirus and the coronavirus that caused the spread of MERS in 2012. Both belong to the coronavirus family and, in the previous case, several studies found specific antibodies in the blood of cured patients.
The similarity between the two viruses prompted scientists to look for antibodies. The study was conducted on 285 patients from three different hospitals. The tests found the presence of specific IgG antibodies 17-19 days after the onset of symptoms in 100% of people. IgM antibodies peak in 94% of patients 20-22 days after symptoms. The maximum level of antibodies remained constant for several times, although in different concentrations in different patients.
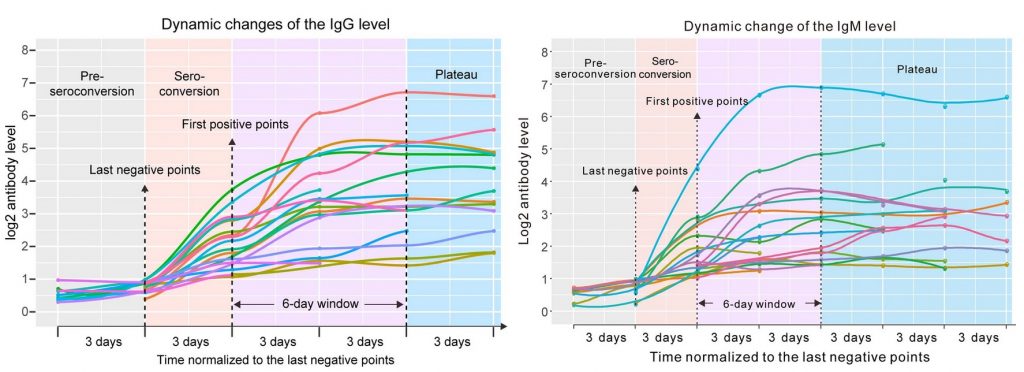
The results are very good news, even if partial, to plan the next steps. The confirmation of antibody production is a great clue to the possibility of achieving SARS-CoV-2 immunity. Single immunity would avoid a relapse in patients already affected in the past and could lead to the famous group immunity following mass vaccination. The study also validates the strategy of serological testing to differentiate people at risk from those immune to the disease.
The study is still partial, the sample of patients is still statistically limited. The final confirmation of the strategies to be implemented will be when the number of patients studied will be greater. Also the type of patients sampled and the sampling time will have to be extended. However, this first confirmation brings a great wave of optimism towards a resolution of the health emergency.